Roger Clarke's Web-Site
© Xamax Consultancy Pty Ltd, 1995-2024

Infrastructure
& Privacy
Matilda
Roger Clarke's Web-Site© Xamax Consultancy Pty Ltd, 1995-2024 |

|
|||||
| HOME | eBusiness |
Information Infrastructure |
Dataveillance & Privacy |
Identity Matters | Other Topics | |
| What's New |
Waltzing Matilda | Advanced Site-Search | ||||
Review Version of 17 March 2019
This is the second article in
a
series on 'Responsible AI', in CLSR.
The first is on
the
issues, and the third on
co-regulation
© Xamax Consultancy Pty Ltd, 2018-19
Available under an AEShareNet ![]() licence or a Creative
Commons
licence or a Creative
Commons  licence.
licence.
This document is at http://www.rogerclarke.com/EC/AIP.html
The first article in this series examined why the world wants controls over Artificial Intelligence (AI). How can an organisation manage AI responsibly, in order to protect its own interests, but also those of its stakeholders and society as a whole? A review of the contributions of ethical analysis extracts limited value. The most effective approach for organisations to take is to apply adapted forms of the established techniques of risk assessment and risk management. Critically, risk assessment needs to be undertaken not only with the organisation's own interests in focus, but also from the perspectives of other stakeholders. To underpin this new form of business process, a set of Principles for Responsible AI is presented, consolidating proposals put forward by over two dozen organisations.
Proponents of Artificial Intelligence (AI) claim that it offers considerable promise, and some forms of it have delivered value. On the other hand, the power inherent in AI naturally harbours substantial threats. The first round of threats afflicts the organisations that develop and deploy AI-based artefacts and systems. The second round of threats impacts upon the many categories of stakeholders involved in and affected by the undertaking. To the extent that the experiences of those stakeholders are negative, and that the stakeholders have power, a third round of threats affects the AI-originating organisations, particularly those that have direct associations with stakeholders, but also those further up the industry supply-chain.
This article adopts the position that it is in the interests of all organisations to avoid their stakeholders suffering harm, and thereby learning to distrust AI and oppose its use. For this to be achieved, organisations need to adopt responsible approaches to AI from the outset. This depends on the inculcation of appropriate culture within the organisation, and the establishment and operation of business processes whose purpose is to detect risk, and manage it.
The article first considers whether business ethics may offer useful insights. A much more useful approach, however, is argued to be through risk assessment and risk management processes. These have traditionally had their focus on the interests of the organisation undertaking the study. Given the impactful nature of AI, this article proposes expansion of risk assessment and risk management in order to encompass not only the organisation's interests but also the stakeholders' perspectives. The final section draws on a diverse set of sources in order to propose a set of principles for the responsible application of AI, which are sufficiently specific to guide organisations' business processes.
Ethics is a branch of philosophy concerned with concepts of right and wrong conduct. Fieser (1995) and Pagallo (2016) distinguish 'meta-ethics', which is concerned with the language, origins, justifications and sources of ethics, from 'normative ethics', which formulates generic norms or standards, and 'applied ethics', which endeavours to operationalise norms in particular contexts.
From the viewpoint of instrumentalists in business and government, the field of ethics evidences several substantial deficiencies. The first is that there is no authority, or at least no uncontestable authority, for any particular formulation of norms, and hence every proposition is subject to debate. Further, as a form of philosophical endeavour, ethics embodies every complexity and contradiction that smart people can dream up. Moreover, few formulations by philosophers ever reach even close to operational guidance, and hence the sources enable prevarication and provide endless excuses for inaction. The inevitable result is that ethical discussions seldom have much influence on real-world behaviour. Ethics is an intellectually stimulating topic for the dinner-table, and graces ex post facto reviews of disasters. However, the notion of 'ethics by design' is even more empty than the 'privacy by design' meme. To an instrumentalist - who wants to get things done - ethics diversions are worse than a time-waster; they're a barrier to progress.
The periodically fashionable topic of 'business ethics' naturally inherits the vagueness of ethics generally (Donaldson & Dunfee 1994, Joyner & Payne 2002). Despite many years of discussion, the absence of any source of authoritative principles results in difficulties structuring concrete guidance for organisations in any of the many areas in which ethical issues are thought to arise. Far less does 'business ethics' assist in relation to complex and opaque digital technologies.
Clarke (2018b) consolidates a collection of attempts to formulate general ethical principles that may have applicability in technology-rich contexts - including bio-medicine, surveillance and information technology. Remarkably, none of them contains any explicit reference to identifying relevant stakeholders. However, a number of norms are apparent in multiple of the documents. These include demonstrated effectiveness and benefits, justification of disbenefits, mitigation of disbenefits, proportionality of negative impacts, supervision (including safeguards, controls and audit), and recourse (including complaints and appeals channels, redress, sanctions, and enforcement powers and resources). These norms will be re-visited in the final section of this article.
The related notion of Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR), sometimes extended to include an Environmental aspect, can be argued to have an ethical base (Carroll 1999). CSR can extend beyond the direct interests of the organisation to include philanthropic contributions to individuals, community, society or the environment. In practice, however, its primary focus appears to most commonly be on the extraction of strategic advantage or public relations gains from organisations' required investments in regulatory compliance and their philanthropic activities (Porter & Kramer 2006).
The potential value of business ethics and CSR as a basis for establishing responsible approaches to AI is constrained by the legal obligations imposed on company directors. Directors are required to act in the best interests of each company of which they are a director. Attention to broad ethical questions is extraneous to, and even in conflict with, that requirement, except where a business case indicates sufficient benefits to the organisation from taking a socially or environmentally responsible approach. In standard texts, stakeholders are mentioned only as a factor in interpreting the director's duty to promote the success of the company (e.g. Keay 2016). Guidance published by corporate regulators, directors' associations and major law firms generally omits mention of either ethics or social responsibility. Even developments in case law are at best only very slowly providing scope for directors to give meaningful consideration to stakeholders' interests (Marshall & Ramsay 2009).
There are secondary, or collateral, ways in which benefits can accrue to stakeholders, through organisations' compliance with regulatory requirements, and the management of relationships and organisational reputation. The categories of stakeholders that are most likely to have sufficient power to attract attention are customers, suppliers and employees, but the scope might extend to communities and economies on which the company has a degree of dependence. But this represents a slim basis on which to build a mechanism to achieve responsible AI.
The remainder of this article pursues more practical avenues. It assumes that organisations, when evaluating AI, apply environmental scanning and marketing techniques in order to identify opportunities, and a business case approach to estimating the strategic, market-share, revenue, cost and profit benefits that the opportunities appear to offer them. The focus here is on how the downsides can be identified, evaluated and managed. Given the considerable investment that each organisation has in its culture, policies and procedures, it is desirable to align the approach as closely as practicable to existing business processes.
This section commences by briefly reviewing the conventional approach to the assessment and management of organisational risks. In order to address the risks that confront stakeholders, I contend that this framework must be extended. Beyond merely identifying stakeholders, the organisation needs to perform risk assessment and management from their perspectives. The second and third sub-sections accordingly consider stakeholder risk assessment and multi-stakeholder risk management.
There are many sources of guidance in relation to organisational risk assessment and management. The techniques are particularly well-developed in the context of the security of IT assets and digital data, although the language and the approaches vary considerably among the many sources (most usefully: Firesmith 2004, ISO 2005, ISO 2008, NIST 2012, ENISA 2016, ISM 2017). For the present purpose, a model is adopted that is summarised in Appendix 1 of Clarke (2015). See Figure 1.
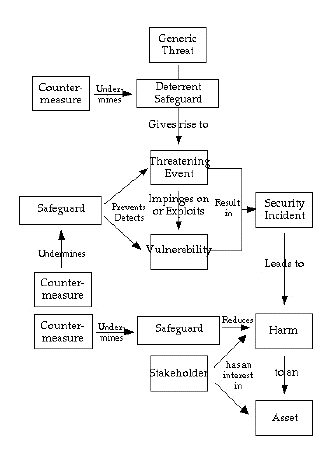
The conventional risk assessment and risk management process is outlined in Table 1. Relevant organisational assets are identified, and an analysis is undertaken of the various forms of harm that could arise to those assets as a result of threats impinging on or actively exploiting vulnerabilities, and giving rise to threatening incidents. Existing safeguards are taken into account, in order to guide the development of a strategy and plan to refine and extend the safeguards and thereby provide a degree of protection that is judged to suitably balance modest actual costs against potentially much higher but contingent costs.
1. Analyse
/
Perform Risk Assessment
1.1 Define the Objectives and Constraints
1.2 Identify the relevant Stakeholders, Assets, Values and categories
of Harm
1.3 Analyse Threats and Vulnerabilities
1.4 Identify existing Safeguards 1.5 Identify and Prioritise the Residual Risks |
2. Design
/
Prepare for Risk Management
2.1 Identify alternative Safeguards
2.2 Evaluate the alternatives against the Objectives and
Constraints 2.3 Select a Design or adapt alternatives to achieve an acceptable Design |
3. Do
/
Perform Risk Management
3.1 Plan the implementation
3.2 Implement 3.3 Review the implementation |
The initial, analysis phase provides the information needed for the strategy, design and planning processes whereby existing safeguards are adapted or replaced and new safeguards conceived and implemented. ISO standard 27005 (2008, pp.20-24) discusses four options for what it refers to as 'risk treatment': risk modification, risk retention, risk avoidance and risk sharing. Table 2 presents a framework that in my experience is more understandable by practitioners and more readily usable as a basis for identifying possible safeguards.
__________________
Conventional approaches to risk assessment and management adopt the perspective of the organisation. The process identifies stakeholders, but their interests are reflected only to the extent that harm to them may result in material harm to the organisation. The focus of this article is on responsible behaviour by organisations in relation to the development and deployment of AI. As discussed in the previous article, AI is potentially highly impactful. Organisations accordingly need to invest much more effort into understanding and addressing the risks faced by their stakeholders.
The term 'stakeholders' was coined, as a counterpoint to 'shareholders', in order to bring those parties' interests into focus (Freeman & Reed 1983). Since the 1970s, employees have been users of the organisation's information systems. IT services now extend beyond organisations' boundaries, and hence many suppliers and customers may be users as well.
The categories of stakeholders are broader than users, however, comprising not only "participants in the information systems development process" but also "any other individuals, groups or organizations whose actions can influence or be influenced by the development and use of the system whether directly or indirectly" (Pouloudi & Whitley 1997, p.3). The term 'usees' is usefully descriptive of such once-removed stakeholders (Clarke 1992, Fischer-Huebner & Lindskog 2001, Baumer 2015). Applications that have usee stakeholders include credit bureau operations, shared databases about tenants and claimants on insurance policies, and intelligence systems operated by law enforcement agencies and private investigators. Further examples of usees include employees' dependants, local communities and the local physical environment, and, in the case of highly impactful IT, regional economies and natural ecologies.
Some AI projects may involve only a single stakeholder group, such as employees. In many contexts, on the other hand, multiple stakeholders need to be recognised. For example, driverless vehicles affect not just pasengers, but also occupants of other vehicles and pedestrians. The individuals in occupations whose existence is threatened by the new approach (e.g. taxi-, courier- and truck-drivers) expect to have a voice. So do their employers, and their unions, and those organisations may have sufficient influence to force their way into a place at the negotiation table. In the case of neural networking models, credit consumers, health insurance clients and welfare recipients may be so incensed by AI-derived discrimination against them that public pressure may force multi-stakeholder approaches onto lenders, health insurers and even welfare agencies - if only through politicians nervous about their electability. In the case of implanted medical devices, not only the patients, but also the various health care professions and health insurers have a stake in AI initiatives.
In the face of such complexity, how can an organisation effectively, but also efficiently, act responsibly in relation to AI projects?
My contention is that conventional organisational risk assessment and risk management processes can be adapted in order to meet the need. My first proposition is that:
The responsible application of AI is only possible if stakeholder analysis is undertaken in order not only to identify the categories of entities that are or may be affected by the particular project, but also to gain insight into those entities' needs and interests
There are well-established techniques for conducting stakeholder analysis (Clarkson 1995, Mitchell et al. 1997, Fletcher et al. 2003). There are also many commercially-published guidance documents. A natural tendency exists to focus on those entities that have sufficient market or institutional power to significantly affect the success of the project. On the other hand, in a world of social media and rapid and deep mood-swings, it is advisable to not overlook the nominally less powerful stakeholders. Where large numbers of individuals are involved (typically, employees, consumers and the general public), it will generally be practical to use representative and advocacy organisations as intermediaries, to speak on behalf of the categories or segments of individuals.
My second proposition is that:
Risk assessment processes that reflect the interests of stakeholders need to be broader than those commonly undertaken within organisations
No term such as 'public risk assessment' appears to have become mainstream, but the concept of 'impact assessment' has. The earliest context was environmenral impacts. Techniques more directly relevant to AI include the longstanding idea of 'technology assessment' (OTA 1977), the little-developed field of social impact assessment (Becker & Vanclay 2003), and the currently very active technique of 'privacy impact assessment' (Clarke 2009, Wright & De Hert 2012). For an example of impact assessment applied to the specific category of person-carrier robots, see Villaronga & Roig (2017).
My third proposition is that:
The responsible application of AI depends on risk assessment processes being conducted from the perspective of each stakeholder group, to complement that undertaken from the organisation's perspective
Such assessments could be conducted by the stakeholders independently, and fed into the organisation. However, the asymmetry of information, resources and power, and the degree of difference in world-views among stakeholder groups, may be so pronounced that the results of such independent activities may be difficult to assimilate and to integrate into the organisation's ways of working.
The organisation may therefore prefer to drive the studies and engage directly with the relevant parties. This can enable the organisation to gain sufficiently deep understanding, and to be able to reflect stakeholders' needs in the project design criteria and features - and to do so without enormous cost to the organisation, and with the minimum harm to its own interests. Medical implants may provide good exemplars of multi-stakeholder risk assessment and management. These involve manufacturers undertaking carefully-designed pilot studies, with active participation by multiple health care professionals, patients, and patient advocacy organisations.
The risk assessment process outlined in Table 1 requires adaptation in order to reflect the broader set of interests under consideration. Table 3 depicts a possible approach.
1. Analyse
/
Perform Risk Assessment
1.1 Define the Objectives and Constraints 1.2 Identify the relevant Stakeholders
| |||
2. Design
/
Prepare for Risk Management
2.1 Identify alternative Safeguards
2.2 Evaluate the alternatives against the Objectives and
Constraints 2.3 Select a Design or adapt / refine the alternatives to achieve an acceptable Design | |||
3. Do
/
Perform Risk Management
3.1 Plan the implementation
3.2 Implement 3.3 Review the implementation |
This section has suggested customisation of existing, generic techniques in order to deal with the substantial impacts of AI-based systems. The following section considers more closely the requirements that need to be satisfied by multi-stakeholder risk management strategies, designs and plans.
The conduct of risk assessment from the perspective of stakeholders depends on the analyst being attuned to those stakeholders' perspectives, interests and needs. This involves understanding and using a quite different vocabulary from that relevant to organisational risk assessment. In addition to those already-substantial challenges, AI is a special case - arguably the most advanced, the most complex, the most mysterious, and the most threatening of all of the leaps forward that IT has gifted and imposed on the public during the 80 years since World War II stimulated invention, innovation and investment in computing.
Despite the frequent periods of public concern about IT, and despite the steady accretion of threats, the formulations of human rights that were negotiated during the post-War period have not yet been revised. So there is no ready-made body of norms, aspirational statements or expressions of moral rights on which risk analysts can depend.
There are, however, some sources of guidance. The bold claims of AI's proponents have generated counter-statements by academics and advocates for the interests of the public. Professional bodies in the IT arena have recently recognised that adaptation and articulation of their Codes of Ethics are long overdue, and have begun programs that are slowly moving beyond discussions and towards the expression of principles. Government bodies and supra-governmental associations have conducted studies. Corporations and industry associations have responded to these developments by uttering warm words of semi-commitment. Raw material exists.
This section presents a set of Principles for Responsible AI. Its purpose is to provide organisations and individual practitioners with guidance as to how they can fulfil their responsibilities in relation to AI technology and AI-based artefacts and systems. They are a natural fit to the needs of multi-stakeholder risk assessment and management as proposed in the previous section, but they are applicable in other contexts, such as social and privacy impact assessment.
The following sub-section outlines the process whereby the Principles were drafted, and identifies the sources used. The main body of the section explains their nature, presents their abstract expression ('The 10 Principles'), and provides access to their more detailed expression ('The 50 Principles'). The final sub-section contains some meta-discussion about the Principles.
The process of developing the set of Principles commenced with the postulation of themes. This was based on prior reading in the the fields of ethics in IT and AI, the analysis reported in the prior article in the present series, including the articulation of threats in s.4 of that article, and preliminary reading of many documents on possible safeguards.
Previously-published sets of principles were then catalogued and inspected. Diversity of perspective was actively sought, through searches in academic, professional and policy literatures. A total of 26 sources was identified and assessed, from governmental organisations (7), non-government organisations (6), corporations and industry associations (5), professional associations (2), joint associations (2), and academics (4). All significant documents that came to light were utilised, with an exception in the area of human rights, where the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR 1966) was included, but not other related treaties, regarding, for example, social and economic rights, and the rights of children, the disabled, refugees and older persons. Only sets that were available in the English language were used, resulting in a strong bias within the suite towards documents that originated in countries whose primary language(s) is or include English. Of the individual documents, 8 are formulations of 'ethical principles and IT' (extracts and citations at Clarke 2018b), and 18 focus on AI specifically (Clarke 2018c).
Detailed propositions within each document were extracted, and allocated to themes, maintaining back-references to the sources. A version containing cross-references is provided as Supplementary Materials. Where items threw doubt on the structure or formulation of the general themes, or on the emergent specific Principles, the schema was adapted in order to sustain coherence and limit the extent to which duplications arise.
Some items that appear in source documents are not reflected in the Principles. For example, 'human dignity' and 'justice' are vague abstractions that need to be unpacked into more specific concepts. In addition, some proposals fall outside the scope of the present work. The items that have been excluded from the set are available as Supplementary Materials.
In the previous article in the series, in s.4.5 and Table 2, distinctions were drawn among the successive phases of the supply-chain, which in turn produce AI technology, AI-based artefacts, AI-based systems, deployments of them, and applications of them. In each case, the relevant category of entity was identified that bears responsibility for negative impacts arising from AI. However, within the 26 sets of principles that were examined, only a few mentioned distinctions among entity-types, and in most cases it has to be interpolated which part of the supply-chain the document is intended to address. For example, the European Parliament (CLA-EP 2016) refers to "design, implementation, dissemination and use", IEEE (2017) to "Manufacturers / operators / owners", GEFA (2016) to "manufacturers, programmers or operators", FLI (2017) to researchers, designers, developers and builders, and ACM (2017) to "Owners, designers, builders, users, and other stakeholders". Remarkably, however, in all of these cases the distinctions were only made within a single Principle rather than being applied to the set as a whole.
Some further observations about the nature of the Principles are offered in the final sub-section. The next section provides a brief preamble, presents the abstract set of 10, and provides access to the detailed set of 50.
The status of the Principles enunciated here is important to appreciate. The purpose is to provide practical suggestions for organisations that are seeking to deal with AI responsibly, in particular by means of multi-stakeholder risk assessment and risk management. The Principles represent guidance as to the expectations of stakeholders, but also of competitors, oversight agencies, regulatory agencies and courts. The Principles are not expressions of law - although in some jurisdictions, in some circumstances, some of them are legal requirements, and more may become so. They are expressions of moral obligations; but no authority exists that can impose such obligations. In addition, all of the Principles are contestable, and in different circumstances any of them may be in conflict with other legal or moral obligations, and with various other interests of various stakeholders.
In Table 4, the 10 themes are declared, and some brief text is provided that is intended to provide orientation to the nature and intent of the Principle. It is recommended that readers first familiarise themselves with this Table. This should ease the task of considering the detailed requirements, which are in Appendix 1 to this article: The 50 Principles.
The following Principles apply to each entity responsible for each phase of AI research, invention, innovation, dissemination and application.
AI offers prospects of considerable benefits and disbenefits. All entities involved in creating and applying AI have obligations to assess its short-term impacts and longer-term implications, to demonstrate the achievability of the postulated benefits, to be proactive in relation to disbenefits, and to involve stakeholders in the process.
Considerable public disquiet exists in relation to the replacement of human decision-making with inhumane decision-making by AI-based artefacts and systems, and displacement of human workers by AI-based artefacts and systems.
Considerable public disquiet exists in relation to the prospect of humans being subject to obscure AI-based processes, and ceding power to AI-based artefacts and systems.
All entities involved in creating and applying AI have obligations to provide safeguards for all human stakeholders, whether as users of AI-based artefacts and systems, or as usees affected by them, and to contribute to human stakeholders' wellbeing.
All entities involved in creating and applying AI have obligations to avoid, prevent and mitigate negative impacts on individuals, and to promote the interests of individuals.
All entities have obligations in relation to due process and procedural fairness. These obligations can only be fulfilled if all entities involved in creating and applying AI ensure that humanly-understandable explanations are available to the people affected by AI-based inferences, decisions and actions.
All entities involved in creating and applying AI have obligations in relation to the quality of business processes, products and outcomes.
All entities involved in creating and applying AI have obligations to ensure resistance to malfunctions (robustness) and recoverability when malfunctions occur (resilience), commensurate with the significance of the benefits, the data's sensitivity, and the potential for harm.
All entities involved in creating and applying AI have obligations in relation to due process and procedural fairness. These obligations can only be fulfilled if each entity is discoverable, and each entity addresses problems as they arise.
All entities involved in creating and applying AI have obligations in relation to due process and procedural fairness. These obligations can only be fulfilled if the entity implements problem-handling processes, and respects and complies with external problem-handling processes.
This sub-section contains a meta-discussion about several important aspects of the Principles. One such aspect is that they have been expressed in imperative mode, i.e. in the form of instructions. This is in order to convey that they require action, rather than being merely desirable characteristics, or factors to be considered, or issues to be debated.
Another consideration is whether the Principles address the threats that were articulated in s.4 of the previous article in the series. In each case, this is achieved by means of a web of interlocking Principles. In particular, autonomy is addressed in 2.1, 2.2, 3.1 and 3.2; data quality in 3.3, 6.2, 7.2 and 7.3; process quality in 1.3, 6.2, 7.6, 7.7, 7.8 and 7.9; transparency in 2.1, 3.5, 6.1, 6.2, 6.3, 8.3 and 10.2; and accountability in 1.6, 1.7, 1.8, 3.1, 3.2, 3.3, 9.1, 9.2, 10.1 and 10.2.
Some commonalities exist across some of the source documents. Overall, however, the main impression is of sparseness, with remarkably limited consensus, particularly given that more than 60 years have passed since AI was first heralded. For example, only 1 document encompassed cyborgisation (GEFA 2016); and only 2 documents referred to the precautionary principle (CLA-EP 2016, GEFA 2016).
An analysis was conducted of the documents' coverage of the Principles. The analysis scored documents liberally, recognising them as delivering on a Principle if the idea was in some way evident, even if only some of the Principle as a whole was addressed, and irrespective of the strength of the prescription. Even then, on average, each of the 50 Principles was reflected in only 5 of the 26 documents; and each of the 26 documents reflected only 9 of the 50 Principles. Moreover, the highest score was a mere 28/50 (56%) - for the most recent document, which was the European Commission's Draft Ethics Guidelines for Trustworthy AI (EC 2018).
Very few of the 50 Principles were detectable in a majority of the documents. Taking as examples a couple of quite basic requirements, only 8/26 documents stipulated 'Conduct impact assessment ...' (Principle 1.4), and 'Ensure people's wellbeing ('beneficence')' (4.3) was evident in just 12/26. Only the following achieved at least half, three of them only just:
Each of the sources naturally reflects the express, implicit and subliminal purposes of the drafters and the organisations on whose behalf they were composed. In some cases, for example, the set primarily addresses just one form of AI, such as robotics or machine-learning. Documents prepared by corporations, industry associations, joint associations and even professional associations tended to adopt the perspective of producer roles, with the interests of other stakeholders often relegated to a secondary consideration. For example, the joint-association Future Life Institute perceives the need for "constructive and healthy exchange between AI researchers and policy-makers", but not for any participation by stakeholders themselves (FLI 2017 at 3). As a result, transparency is constrained to a small sub-set of circumstances (at 6), the degree of 'responsibility' of 'designers and builders' is limited to those roles being mere 'stakeholders in moral implications' (at 9), alignment with human values is seen as being necessary only in respect of "highly autonomous AI systems" (at 10, emphasis added), and "strict safety and control measures" are limited to a small sub-set of AI systems (at 22).
The authors of ITIC (2017) consider that many responsibilities lie elsewhere, and responsibilities are assigned to its members only in respect of safety, controllability and data quality. ACM (2017) is expressed in weak language (should be aware of, should encourage, are encouraged) and regards decision opaqueness as being acceptable, while IEEE (2017) suggests a range of important tasks for other parties (standards-setters, regulators, legislatures, courts), and phrases other suggestions in the passive voice, with the result that few obligations are clearly identified as falling on engineering professionals and the organisations that employ them. The House of Lords report (HOL 2018) might have been expected to adopt a societal or multi-stakeholder approach, yet it appears to have adopted the perspective of the AI industry.
Some of the Principles require somewhat different application in each phase of the AI supply-chain. An important example of this is the manner in which Principle 7 - Deliver Transparency and Auditability - is intended to be interpreted. In the Research and Invention phases of the technological life-cycle, compliance with Principle 7 requires understanding by inventors and innovators of the AI technology, and explicability to developers and users of AI-based artefacts and systems. During the Innovation and Dissemination phases, the need is for understandability and manageability by developers and users of AI-based systems and applications, and explicability to affected stakeholders. In the Application phase, the emphasis shifts to understandability by affected stakeholders of inferences, decisions and actions arising from at least the AI elements within AI-based systems and applications.
The Principles are intentionally framed and phrased in a reasonably general manner, in an endeavour to achieve applicability to at least the AI technologies discussed in the first article in the series - robotics, particularly remote-controlled and self-driving vehicles; cyborgs who incorporate computational capabilities; rule-based expert systems; and AI/ML/neural-networking applications. More broadly, the intention is that the Principles be applicable to what I proposed in the first article in the series as more appropriate conceptualisations of the field - Complementary Artefact Intelligence, and Intellectics.
The abstract Principles are capable of being further articulated into much more specific guidance in respect of each particular AI technology. For example, in a companion project, I have proposed 'Guidelines for Responsible Data Analytics' (Clarke 2018a). These provide more detailed guidance for the conduct of all forms of data analytics projects, including those that apply AI/ML/neural-networking approaches. Areas addressed by the Data Analytics guidelines include governance, expertise and compliance considerations, multiple aspects of data acquisition and data quality, the suitability of both the data and the analytical techniques applied to it, and factors involved in the use of inferences drawn from the analysis.
AI technologies emerge from research laboratories offering potential, but harbouring considerable threats to both organisations and their stakeholders. The first article in this series examined why there is public demand for controls over AI, and argued that organisations need to adopt, and to demonstrate publicly that they have adopted, responsible approaches to AI.
This article has formulated guidance for organisations, in both the private and public sectors, whereby they can evaluate the appropriateness of AI technologies to their own operations. Ethical analysis does not deliver what organisations need. Adapted forms of risk assessment and risk management processes have been proposed to meet the requirements. A set of Principles for Responsible AI has been presented, based on over two dozen documents from diverse sources.
I believe that these Principles are suitable for application by executives, managers and professionals, as they stand. They can also be used as a basis for review by internal and external auditors. They are appropriate as a measuring stick for the evaluation of proposals for organisational procedures, industry codes, and legislation, or as a template for the expression of such documents. Further, the Principles can be articulated into more specific expressions that are directly relevant to particular categories of technology, artefacts, systems and applications.
The third article in this series considers how policy-makers can structure a regulatory regime to ensure that, whether or not individual organisations approach AI in a responsible manner, important public interests can be protected.
See here for a PDF version of this Appendix
The following Principles apply to each entity responsible for each phase of AI research, invention, innovation, dissemination and application.
1.1 Conceive and design only after ensuring adequate understanding of purposes and contexts
1.2 Justify objectives
1.3 Demonstrate the achievability of postulated benefits
1.4 Conduct impact assessment, including risk assessment from all stakeholders' perspectives
1.5 Publish sufficient information to stakeholders to enable them to conduct their own assessments
1.6 Conduct consultation with stakeholders and enable their participation in design
1.7 Reflect stakeholders' justified concerns in the design
1.8 Justify negative impacts on individuals ('proportionality')
1.9 Consider alternative, less harmful ways of achieving the same objectives
2.1 Design as an aid, for augmentation, collaboration and inter-operability
2.2 Avoid design for replacement of people by independent artefacts or systems, except in circumstances in which those artefacts or systems are demonstrably more capable than people, and even then ensuring that the result is complementary to human capabilities
3.1 Ensure human control over AI-based technology, artefacts and systems
3.2 In particular, ensure human control over autonomous behaviour of AI-based technology, artefacts and systems
3.3 Respect people's expectations in relation to personal data protections,
including:
* their awareness of data-usage
* their consent
*
data minimisation
* public visibility and design consultation and
participation
* the relationship between data-usage and the data's
original purpose
3.4 Respect each person's autonomy, freedom of choice and right to self-determination
3.5 Ensure human review of inferences and decisions prior to action being taken
3.6 Avoid deception of humans
3.7 Avoid services being conditional on the acceptance of AI-based artefacts and systems
4.1 Ensure people's physical health and safety ('nonmaleficence')
4.2 Ensure people's psychological safety, by avoiding negative effects on their mental health, emotional state, inclusion in society, worth, and standing in comparison with other people
4.3 Contribute to people's wellbeing ('beneficence')
4.4 Implement safeguards to avoid, prevent and mitigate negative impacts and implications
4.5 Avoid violation of trust
4.6 Avoid the manipulation of vulnerable people , e.g. by taking advantage of individuals' tendencies to addictions such as gambling, and to letting pleasure overrule rationality
5.1 Be just / fair / impartial, treat individuals equally, and avoid unfair discrimination and bias, not only where they are illegal, but also where they are materially inconsistent with public expectations
5.2 Ensure compliance with human rights laws
5.3 Avoid restrictions on, and promote, people's freedom of movement
5.4 Avoid interference with, and promote privacy, family, home or reputation
5.5 Avoid interference with, and promote, the rights of freedom of information, opinion and expression, of freedom of assembly, of freedom of association, of freedom to participate in public affairs, and of freedom to access public services
5.6 Where interference with human values or human rights is outweighed by other factors, ensure that the interference is no greater than is justified ('harm minimisation')
6.1 Ensure that the fact that a process is AI-based is transparent to all stakeholders
6.2 Ensure that data provenance, and the means whereby inferences are drawn from it, decisions are made, and actions are taken, are logged and can be reconstructed
6.3 Ensure that people are aware of inferences, decisions and actions that affect them, and have access to humanly-understandable explanations of how they came about
7.1 Ensure effective, efficient and adaptive performance of intended functions
7.2 Ensure data quality and data relevance
7.3 Justify the use of data, commensurate with each data-item's sensitivity
7.4 Ensure security safeguards against inappropriate data access, modification and deletion, commensurate with its sensitivity
7.5 Deal fairly with people ('faithfulness', 'fidelity')
7.6 Ensure that inferences are not drawn from data using invalid or unvalidated techniques
7.7 Test result validity, and address the problems that are detected
7.8 Impose controls in order to ensure that the safeguards are in place and effective
7.9 Conduct audits of safeguards and controls
8.1 Deliver and sustain appropriate security safeguards against the risk of compromise of intended functions arising from both passive threats and active attacks, commensurate with the significance of the benefits and the potential to cause harm
8.2 Deliver and sustain appropriate security safeguards against the risk of inappropriate data access, modification and deletion, arising from both passive threats and active attacks, commensurate with the data's sensitivity
8.3 Conduct audits of the justification, the proportionality, the transparency, and the harm avoidance, prevention and mitigation measures and controls
8.4 Ensure resilience, in the sense of prompt and effective recovery from incidents
9.1 Ensure that the responsible entity is apparent or can be readily discovered by any party
9.2 Ensure that effective remedies exist, in the form of complaints processes, appeals processes, and redress where harmful errors have occurred
10.1 Ensure that complaints, appeals and redress processes operate effectively
10.2 Comply with external complaints, appeals and redress processes and outcomes, including, in particular, provision of timely, accurate and complete information relevant to cases
ACM (2017) 'Statement on Algorithmic Transparency and Accountability' Association for Computing Machinery, January 2017, at https://www.acm.org/binaries/content/assets/public-policy/2017_usacm_statement_algorithms.pdf
Baumer E.P.S. (2015) 'Usees' Proc. 33rd Annual ACM Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (CHI'15), April 2015
Becker H. & Vanclay F. (2003) 'The International Handbook of Social Impact Assessment' Cheltenham: Edward Elgar, 2003
Carroll A.B. (1999) 'Corporate social responsibility: Evolution of a Definitional Construct' Business and Society 38, 3 (Sep 1999) 268-295
CLA-EP (2016) 'Recommendations on Civil Law Rules on Robotics' Committee on Legal Affairs of the European Parliament, 31 May 2016, at http://www.europarl.europa.eu/sides/getDoc.do?pubRef=-//EP//NONSGML%2BCOMPARL%2BPE-582.443%2B01%2BDOC%2BPDF%2BV0//EN
Clarke R. (1992) 'Extra-Organisational Systems: A Challenge to the Software Engineering Paradigm' Proc. IFIP World Congress, Madrid, September 1992, at http://www.rogerclarke.com/SOS/PaperExtraOrgSys.html
Clarke R. (2009) 'Privacy Impact Assessment: Its Origins and Development' Computer Law & Security Review 25, 2 (April 2009) 123-135, PrePrint at http://www.rogerclarke.com/DV/PIAHist-08.html
Clarke R. (2015) 'The Prospects of Easier Security for SMEs and Consumers' Computer Law & Security Review 31, 4 (August 2015) 538-552, PrePrint at http://www.rogerclarke.com/EC/SSACS.html
Clarke R. (2018a) 'Guidelines for the Responsible Application of Data
Analytics' Computer Law & Security Review 34, 3 (May-Jun 2018) 467- 476,
PrePrint at
http://www.rogerclarke.com/EC/GDA.html
Clarke R. (2018b) 'Ethical Principles and Information Technology' Xamax
Consultancy Pty Ltd, rev. September 2018, at
http://www.rogerclarke.com/EC/GAIE.html
Clarke R. (2018c) 'Principles for AI: A 2017-18 SourceBook' Xamax Consultancy
Pty Ltd, rev. September 2018, at
http://www.rogerclarke.com/EC/GAIP.html
Clarkson M.B.E. (1995) 'A Stakeholder Framework for Analyzing and Evaluating Corporate Social Performance' The Academy of Management Review 20, 1 (Jan.1995) 92-117 , at https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Mei_Peng_Low/post/Whats_corporate_social_performance_related_to_CSR/attachment/59d6567879197b80779ad3f2/AS%3A530408064417792%401503470545971/download/A_Stakeholder_Framework_for_Analyzing+CSP.pdf
Donaldson T. & Dunfee T.W. (1994) 'Toward a Unified Conception of Business Ethics: Integrative Social Contracts Theory' Academy ofManagement Review 19, 2 (Apr 1994) 252-284
EC (2018) 'Statement on Artificial Intelligence, Robotics and `Autonomous' Systems' European Group on Ethics in Science and New Technologies' European Commission, March 2018, at http://ec.europa.eu/research/ege/pdf/ege_ai_statement_2018.pdf
ENISA (2016) 'Risk Management:Implementation principles and Inventories for Risk Management/Risk Assessment methods and tools' European Union Agency for Network and Information Security, June 2016, at https://www.enisa.europa.eu/publications/risk-management-principles-and-inventories-for-risk-management-risk-assessment-methods-and-tools
Fieser J. (1995) 'Ethics' Internet Encyclopaedia of Philosophy, 1995, at https://www.iep.utm.edu/ethics/
Firesmith D. (2004) 'Specifying Reusable Security Requirements' Journal of Object Technology 3, 1 (Jan-Feb 2004) 61-75, at http://www.jot.fm/issues/issue_2004_01/column6
Fischer-Huebner S. & Lindskog H. (2001) 'Teaching Privacy-Enhancing Technologies' Proc. IFIP WG 11.8 2nd World Conference on Information Security Education, Perth, 2001, at http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.24.3950&rep=rep1&type=pdf
Fletcher A., Guthrie J., Steane P., Roos G. & Pike S. (2003) 'Mapping stakeholder perceptions for a third sector organization' Journal of Intellectual Capital 4,4 (2003) 505-527
FLI (2017) 'Asilomar AI Principles' Future of Life Institute, January 2017, at https://futureoflife.org/ai-principles/?cn-reloaded=1
Freeman R.E. & Reed D.L. (1983) 'Stockholders and Stakeholders: A New Perspective on Corporate Governance' California Management Review 25:, 3 (1983) 88-106, at https://www.researchgate.net/profile/R_Freeman/publication/238325277_Stockholders_and_Stakeholders_A_New_Perspective_on_Corporate_Governance/links/5893a4b2a6fdcc45530c2ee7/Stockholders-and-Stakeholders-A-New-Perspective-on-Corporate-Governance.pdf
GEFA (2016) 'Position on Robotics and AI' The Greens / European Free Alliance Digital Working Group, November 2016, at https://juliareda.eu/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/Green-Digital-Working-Group-Position-on-Robotics-and-Artificial-Intelligence-2016-11-22.pdf
HOL (2018) 'AI in the UK: ready, willing and able?' Select Committee on Artificial Intelligence, House of Lords, April 2018, at https://publications.parliament.uk/pa/ld201719/ldselect/ldai/100/100.pdf
ICCPR (1966) 'International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights' United Nations, 1966, at http://www.ohchr.org/en/professionalinterest/pages/ccpr.aspx
IEEE (2017) 'Ethically Aligned Design: A Vision for Prioritizing Human Well-being with Autonomous and Intelligent Systems (A/IS)' IEEE, Version 2, December 2017, at http://standards.ieee.org/develop/indconn/ec/autonomous_systems.html
ISM (2017) 'Information Security Manual' Australian Signals Directorate, November 2017, at https://acsc.gov.au/infosec/ism/index.htm
ISO (2005) 'Information Technology - Code of practice for information security management', International Standards Organisation, ISO/IEC 27002:2005
ISO (2008) 'Information Technology - Security Techniques - Information Security Risk Management' ISO/IEC 27005:2008
ITIC (2017) 'AI Policy Principles' Information Technology Industry Council, undated but apparently of October 2017, at https://www.itic.org/resources/AI-Policy-Principles-FullReport2.pdf
Joyner B.E. & Payne D. (2002) 'Evolution and Implementation: A Study of Values, Business Ethics and Corporate Social Responsibility' Journal of Business Ethics 41, 4 (December 2002) 297-311
Keay A. (2016) 'Directors' Duties' Lexis-Nexis, 2016
Marshall S. & Ramsay I. (2009) 'Shareholders and Directors' Duties: Law, Theory and Evidence' Legal Studies Research Paper No. 411, Melbourne Law School, University of Melbourne, June 2009, at https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=1402143
Mitchell R.K., Agle B.R. & Wood D.J. (1997) 'Toward a Theory of Stakeholder Identification and Salience: Defining the Principle of Who and What Really Counts' The Academy of Management Review 22,4 (October 1997) 853-886
NIST (2012) 'Guide for Conducting Risk Assessments' National Institute of Standards and Technology, Special Publication SP 800-30 Rev. 1, September 2012, at http://csrc.nist.gov/publications/nistpubs/800-30-rev1/sp800_30_r1.pdf
OTA (1977) 'Technology Assessment in Business and Government' Office of Technology Assessment, NTIS order #PB-273164', January 1977, at http://www.princeton.edu/~ota/disk3/1977/7711_n.html
Pagallo U. (2016). 'Even Angels Need the Rules: AI, Roboethics, and the Law' Proc. ECAI 2016
Porter M.E. & Kramer M.R. (2006) 'The Link Between Competitive Advantage and Corporate Social Responsibility' Harvard Business Review 84, 12 (December 2006) 78-92
Pouloudi A. & Whitley E.A. (1997) 'Stakeholder Identification in Inter-Organizational Systems: Gaining Insights for Drug Use Management Systems' European Journal of Information Systems 6, 1 (1997) 1-14, at http://eprints.lse.ac.uk/27187/1/__lse.ac.uk_storage_LIBRARY_Secondary_libfile_shared_repository_Content_Whitley_Stakeholder%20identification_Whitley_Stakeholder%20identification_2015.pdf
Villaronga E.F. & Roig A. (2017) 'European regulatory framework for person carrier robots' Computer Law & Security Review 33, 4 (Jul-Aug 2017) 502-220
Wright D. & De Hert P. (eds) (2012) 'Privacy Impact Assessments' Springer, 2012
This paper has benefited from feedback from multiple colleagues, and particularly Peter Leonard of Data Synergies and Prof. Graham Greenleaf and Kayleen Manwaring of UNSW.
Roger Clarke is Principal of Xamax Consultancy Pty Ltd, Canberra. He is also a Visiting Professor in Cyberspace Law & Policy at the University of N.S.W., and a Visiting Professor in the Research School of Computer Science at the Australian National University. He has also spent many years on the Board of the Australian Privacy Foundation, and is Company Secretary of the Internet Society of Australia.
| Personalia |
Photographs Presentations Videos |
Access Statistics |
 |
The content and infrastructure for these community service pages are provided by Roger Clarke through his consultancy company, Xamax. From the site's beginnings in August 1994 until February 2009, the infrastructure was provided by the Australian National University. During that time, the site accumulated close to 30 million hits. It passed 65 million in early 2021. Sponsored by the Gallery, Bunhybee Grasslands, the extended Clarke Family, Knights of the Spatchcock and their drummer |
Xamax Consultancy Pty Ltd ACN: 002 360 456 78 Sidaway St, Chapman ACT 2611 AUSTRALIA Tel: +61 2 6288 6916 |
Created: 11 July 2018 - Last Amended: 17 March 2019 by Roger Clarke - Site Last Verified: 15 February 2009
This document is at www.rogerclarke.com/EC/AIP-190317.html
Mail to Webmaster - © Xamax Consultancy Pty Ltd, 1995-2022 - Privacy Policy